gitlab-ce
configMap
아래 파일을 gitlab.rb 로 저장하고 gitlab-config라는 이름의 configmap 생성하자.
###############################################
# Custom Setting by Supermoon Begin #
###############################################
external_url '<사용할 git 주소, https>'
nginx['listen_port'] = 80
nginx['listen_https'] = false
puma['worker_processes'] = 0
prometheus['enable'] = false
alertmanager['enable'] = false
redis_exporter['enable'] = false
postgres_exporter['enable'] = false
gitlab_exporter['enable'] = false
###############################################
# Custom Setting by Supermoon End #
###############################################
## 이하는 default gitlab.rb 와 동일 ##
## GitLab configuration settings
##! This file is generated during initial installation and **is not** modified
##! during upgrades.
##! Check out the latest version of this file to know about the different
##! settings that can be configured, when they were introduced and why:
##! https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/blame/master/files/gitlab-config-template/gitlab.rb.template
##! Locally, the complete template corresponding to the installed version can be found at:
##! /opt/gitlab/etc/gitlab.rb.template
##! You can run `gitlab-ctl diff-config` to compare the contents of the current gitlab.rb with
##! the gitlab.rb.template from the currently running version.
##! You can run `gitlab-ctl show-config` to display the configuration that will be generated by
##! running `gitlab-ctl reconfigure`
##! In general, the values specified here should reflect what the default value of the attribute will be.
##! There are instances where this behavior is not possible or desired. For example, when providing passwords,
##! or connecting to third party services.
##! In those instances, we endeavour to provide an example configuration.
## GitLab URL
##! URL on which GitLab will be reachable.
##! For more details on configuring external_url see:
##! https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#configuring-the-external-url-for-gitlab
##!
##! Note: During installation/upgrades, the value of the environment variable
##! EXTERNAL_URL will be used to populate/replace this value.
##! On AWS EC2 instances, we also attempt to fetch the public hostname/IP
##! address from AWS. For more details, see:
##! https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/instancedata-data-retrieval.html
# external_url 'GENERATED_EXTERNAL_URL'
## Roles for multi-instance GitLab
##! The default is to have no roles enabled, which results in GitLab running as an all-in-one instance.
##! Options:
##! redis_sentinel_role redis_master_role redis_replica_role geo_primary_role geo_secondary_role
##! postgres_role consul_role application_role monitoring_role
##! For more details on each role, see:
##! https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/roles/index.html#roles
##!
# roles ['redis_sentinel_role', 'redis_master_role']
## Legend
##! The following notations at the beginning of each line may be used to
##! differentiate between components of this file and to easily select them using
##! a regex.
##! ## Titles, subtitles etc
##! ##! More information - Description, Docs, Links, Issues etc.
##! Configuration settings have a single # followed by a single space at the
##! beginning; Remove them to enable the setting.
##! **Configuration settings below are optional.**
################################################################################
################################################################################
## Configuration Settings for GitLab CE and EE ##
################################################################################
################################################################################
################################################################################
## gitlab.yml configuration
##! Docs: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/omnibus-gitlab/blob/master/doc/settings/gitlab.yml.md
################################################################################
# gitlab_rails['enable'] = true # do not disable unless explicitly told to do so in docs
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_ssh_host'] = 'ssh.host_example.com'
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_ssh_user'] = ''
# gitlab_rails['time_zone'] = 'UTC'
### Rails asset / CDN host
###! Defines a url for a host/cdn to use for the Rails assets
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#set-a-content-delivery-network-url
# gitlab_rails['cdn_host'] = 'https://mycdnsubdomain.fictional-cdn.com'
### Request duration
###! Tells the rails application how long it has to complete a request
###! This value needs to be lower than the worker timeout set in puma.
###! By default, we'll allow 95% of the the worker timeout
# gitlab_rails['max_request_duration_seconds'] = 57
### GitLab email server settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/smtp.html
###! **Use smtp instead of sendmail/postfix.**
# gitlab_rails['smtp_enable'] = true
# gitlab_rails['smtp_address'] = "smtp.server"
# gitlab_rails['smtp_port'] = 465
# gitlab_rails['smtp_user_name'] = "smtp user"
# gitlab_rails['smtp_password'] = "smtp password"
# gitlab_rails['smtp_domain'] = "example.com"
# gitlab_rails['smtp_authentication'] = "login"
# gitlab_rails['smtp_enable_starttls_auto'] = true
# gitlab_rails['smtp_tls'] = false
# gitlab_rails['smtp_pool'] = false
###! **Can be: 'none', 'peer', 'client_once', 'fail_if_no_peer_cert'**
###! Docs: http://api.rubyonrails.org/classes/ActionMailer/Base.html
# gitlab_rails['smtp_openssl_verify_mode'] = 'none'
# gitlab_rails['smtp_ca_path'] = "/etc/ssl/certs"
# gitlab_rails['smtp_ca_file'] = "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt"
### Email Settings
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_enabled'] = true
##! If your SMTP server does not like the default 'From: gitlab@gitlab.example.com'
##! can change the 'From' with this setting.
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_from'] = 'example@example.com'
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_display_name'] = 'Example'
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_reply_to'] = 'noreply@example.com'
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_subject_suffix'] = ''
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_smime_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_smime_key_file'] = '/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab_smime.key'
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_smime_cert_file'] = '/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab_smime.crt'
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_email_smime_ca_certs_file'] = '/etc/gitlab/ssl/gitlab_smime_cas.crt'
### GitLab user privileges
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_username_changing_enabled'] = true
### Default Theme
### Available values:
##! `1` for Indigo
##! `2` for Dark
##! `3` for Light
##! `4` for Blue
##! `5` for Green
##! `6` for Light Indigo
##! `7` for Light Blue
##! `8` for Light Green
##! `9` for Red
##! `10` for Light Red
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_theme'] = 2
### Custom html header tags
###! See https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/custom_html_header_tags.html for more
# In some cases some custom header tags are needed
# e.g., to add the EU cookie consent
# Tip: you must add the externals source to the content_security_policy as
# well, typically the script_src and style_src.
# gitlab_rails['custom_html_header_tags'] = nil
### Default project feature settings
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_projects_features_issues'] = true
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_projects_features_merge_requests'] = true
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_projects_features_wiki'] = true
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_projects_features_snippets'] = true
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_projects_features_builds'] = true
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_default_projects_features_container_registry'] = true
### Automatic issue closing
###! See https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/issue_closing_pattern.html for more
###! information about this pattern.
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_issue_closing_pattern'] = "\b((?:[Cc]los(?:e[sd]?|ing)|\b[Ff]ix(?:e[sd]|ing)?|\b[Rr]esolv(?:e[sd]?|ing)|\b[Ii]mplement(?:s|ed|ing)?)(:?) +(?:(?:issues? +)?%{issue_ref}(?:(?:, *| +and +)?)|([A-Z][A-Z0-9_]+-\d+))+)"
### Download location
###! When a user clicks e.g. 'Download zip' on a project, a temporary zip file
###! is created in the following directory.
###! Should not be the same path, or a sub directory of any of the `git_data_dirs`
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_repository_downloads_path'] = 'tmp/repositories'
### Gravatar Settings
# gitlab_rails['gravatar_plain_url'] = 'http://www.gravatar.com/avatar/%{hash}?s=%{size}&d=identicon'
# gitlab_rails['gravatar_ssl_url'] = 'https://secure.gravatar.com/avatar/%{hash}?s=%{size}&d=identicon'
### Auxiliary jobs
###! Periodically executed jobs, to self-heal Gitlab, do external
###! synchronizations, etc.
###! Docs: https://github.com/ondrejbartas/sidekiq-cron#adding-cron-job
###! https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/yaml/index.html#artifactsexpire_in
# gitlab_rails['stuck_ci_jobs_worker_cron'] = "0 0 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['expire_build_artifacts_worker_cron'] = "*/7 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['environments_auto_stop_cron_worker_cron'] = "24 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['pipeline_schedule_worker_cron'] = "19 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ci_archive_traces_cron_worker_cron'] = "17 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['repository_check_worker_cron'] = "20 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['admin_email_worker_cron'] = "0 0 * * 0"
# gitlab_rails['personal_access_tokens_expiring_worker_cron'] = "0 1 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['personal_access_tokens_expired_notification_worker_cron'] = "0 2 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['repository_archive_cache_worker_cron'] = "0 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['pages_domain_verification_cron_worker'] = "*/15 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['pages_domain_ssl_renewal_cron_worker'] = "*/10 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['pages_domain_removal_cron_worker'] = "47 0 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['remove_unaccepted_member_invites_cron_worker'] = "10 15 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['schedule_migrate_external_diffs_worker_cron'] = "15 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ci_platform_metrics_update_cron_worker'] = '47 9 * * *'
# gitlab_rails['analytics_usage_trends_count_job_trigger_worker_cron'] = "50 23 */1 * *"
# gitlab_rails['member_invitation_reminder_emails_worker_cron'] = "0 0 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['user_status_cleanup_batch_worker_cron'] = "* * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['namespaces_in_product_marketing_emails_worker_cron'] = "0 9 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ssh_keys_expired_notification_worker_cron'] = "0 2 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ssh_keys_expiring_soon_notification_worker_cron'] = "0 1 * * *"
# gitlab_rails['loose_foreign_keys_cleanup_worker_cron'] = "*/5 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ci_runner_versions_reconciliation_worker_cron'] = "@daily"
# gitlab_rails['ci_runners_stale_machines_cleanup_worker_cron'] = "36 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ci_catalog_resources_process_sync_events_worker_cron'] = "*/1 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ci_click_house_finished_pipelines_sync_worker_cron'] = "*/4 * * * *"
# gitlab_rails['ci_click_house_finished_pipelines_sync_worker_args'] = [1]
### Webhook Settings
###! Number of seconds to wait for HTTP response after sending webhook HTTP POST
###! request (default: 10)
# gitlab_rails['webhook_timeout'] = 10
### HTTP client settings
###! This is for setting up the mutual TLS client cert and password for the certificate file.
# gitlab_rails['http_client']['tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['http_client']['tls_client_cert_password'] = nil
### GraphQL Settings
###! Tells the rails application how long it has to complete a GraphQL request.
###! We suggest this value to be higher than the database timeout value
###! and lower than the worker timeout set in puma. (default: 30)
# gitlab_rails['graphql_timeout'] = 30
### Trusted proxies
###! Customize if you have GitLab behind a reverse proxy which is running on a
###! different machine.
###! **Add the IP address for your reverse proxy to the list, otherwise users
###! will appear signed in from that address.**
# gitlab_rails['trusted_proxies'] = []
### Content Security Policy
####! Customize if you want to enable the Content-Security-Policy header, which
####! can help thwart JavaScript cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
####! See: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP
# gitlab_rails['content_security_policy'] = {
# 'enabled' => false,
# 'report_only' => false,
# # Each directive is a String (e.g. "'self'").
# 'directives' => {
# 'base_uri' => nil,
# 'child_src' => nil,
# 'connect_src' => nil,
# 'default_src' => nil,
# 'font_src' => nil,
# 'form_action' => nil,
# 'frame_ancestors' => nil,
# 'frame_src' => nil,
# 'img_src' => nil,
# 'manifest_src' => nil,
# 'media_src' => nil,
# 'object_src' => nil,
# 'script_src' => nil,
# 'style_src' => nil,
# 'worker_src' => nil,
# 'report_uri' => nil,
# }
# }
### Allowed hosts
###! Customize the `host` headers that should be catered by the Rails
###! application. By default, everything is allowed.
# gitlab_rails['allowed_hosts'] = []
### Monitoring settings
###! IP whitelist controlling access to monitoring endpoints
# gitlab_rails['monitoring_whitelist'] = ['127.0.0.0/8', '::1/128']
### Shutdown settings
###! Defines an interval to block healthcheck,
###! but continue accepting application requests.
# gitlab_rails['shutdown_blackout_seconds'] = 10
### Microsoft Graph Mailer
###! Allows delivery of emails using Microsoft Graph API with OAuth 2.0 client
###! credentials flow.
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/microsoft_graph_mailer.html
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_user_id'] = "YOUR-USER-ID"
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_tenant'] = "YOUR-TENANT-ID"
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_client_id'] = "YOUR-CLIENT-ID"
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_client_secret'] = "YOUR-CLIENT-SECRET-ID"
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_azure_ad_endpoint'] = "https://login.microsoftonline.com"
# gitlab_rails['microsoft_graph_mailer_graph_endpoint'] = "https://graph.microsoft.com"
### Reply by email
###! Allow users to comment on issues and merge requests by replying to
###! notification emails.
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/reply_by_email.html
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_enabled'] = true
#### Incoming Email Address
####! The email address including the `%{key}` placeholder that will be replaced
####! to reference the item being replied to.
####! **The placeholder can be omitted but if present, it must appear in the
####! "user" part of the address (before the `@`).**
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_address'] = "gitlab-incoming+%{key}@gmail.com"
#### Email account username
####! **With third party providers, this is usually the full email address.**
####! **With self-hosted email servers, this is usually the user part of the
####! email address.**
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_email'] = "gitlab-incoming@gmail.com"
#### Email account password
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_password'] = "[REDACTED]"
#### IMAP Settings
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_host'] = "imap.gmail.com"
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_port'] = 993
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_ssl'] = true
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_start_tls'] = false
#### Incoming Mailbox Settings (via `mail_room`)
####! The mailbox where incoming mail will end up. Usually "inbox".
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_mailbox_name'] = "inbox"
####! The IDLE command timeout.
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_idle_timeout'] = 60
####! The file name for internal `mail_room` JSON logfile
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_log_file'] = "/var/log/gitlab/mailroom/mail_room_json.log"
####! This marks incoming messages deleted after delivery.
####! If you are using Microsoft Graph API instead of IMAP, set this to false to retain
####! messages in the inbox since deleted messages are auto-expunged after some time.
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_delete_after_delivery'] = true
####! Permanently remove messages from the mailbox when they are marked as deleted after delivery
####! Only applies to IMAP. Microsoft Graph will auto-expunge any deleted messages.
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_expunge_deleted'] = false
#### Inbox options (for Microsoft Graph)
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_inbox_method'] = 'microsoft_graph'
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_inbox_options'] = {
# 'tenant_id': 'YOUR-TENANT-ID',
# 'client_id': 'YOUR-CLIENT-ID',
# 'client_secret': 'YOUR-CLIENT-SECRET',
# 'poll_interval': 60 # Optional
# }
#### How incoming emails are delivered to Rails process. Accept either sidekiq
#### or webhook. The default config is webhook.
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_delivery_method'] = "webhook"
#### Token to authenticate webhook requests. The token must be exactly 32 bytes,
#### encoded with base64
# gitlab_rails['incoming_email_auth_token'] = nil
####! The format of mail_room crash logs
# mailroom['exit_log_format'] = "plain"
### Consolidated (simplified) object storage configuration
###! This uses a single credential for object storage with multiple buckets.
###! It also enables Workhorse to upload files directly with its own S3 client
###! instead of using pre-signed URLs.
###!
###! This configuration will only take effect if the object_store
###! sections are not defined within the types. For example, enabling
###! gitlab_rails['artifacts_object_store_enabled'] or
###! gitlab_rails['lfs_object_store_enabled'] will prevent the
###! consolidated settings from being used.
###!
###! Be sure to use different buckets for each type of object.
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/object_storage.html
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['connection'] = {}
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['storage_options'] = {}
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['proxy_download'] = false
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['artifacts']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['external_diffs']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['lfs']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['uploads']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['packages']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['dependency_proxy']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['terraform_state']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['ci_secure_files']['bucket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['object_store']['objects']['pages']['bucket'] = nil
### Job Artifacts
# gitlab_rails['artifacts_enabled'] = true
# gitlab_rails['artifacts_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/artifacts"
####! Job artifacts Object Store
####! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/job_artifacts.html#using-object-storage
# gitlab_rails['artifacts_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['artifacts_object_store_proxy_download'] = false
# gitlab_rails['artifacts_object_store_remote_directory'] = "artifacts"
# gitlab_rails['artifacts_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
### External merge request diffs
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_when'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_storage_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/external-diffs"
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_object_store_proxy_download'] = false
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_object_store_remote_directory'] = "external-diffs"
# gitlab_rails['external_diffs_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
### Git LFS
# gitlab_rails['lfs_enabled'] = true
# gitlab_rails['lfs_storage_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/lfs-objects"
# gitlab_rails['lfs_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['lfs_object_store_proxy_download'] = false
# gitlab_rails['lfs_object_store_remote_directory'] = "lfs-objects"
# gitlab_rails['lfs_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
### GitLab uploads
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/uploads.html
# gitlab_rails['uploads_directory'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/uploads"
# gitlab_rails['uploads_storage_path'] = "/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/public"
# gitlab_rails['uploads_base_dir'] = "uploads/-/system"
# gitlab_rails['uploads_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['uploads_object_store_proxy_download'] = false
# gitlab_rails['uploads_object_store_remote_directory'] = "uploads"
# gitlab_rails['uploads_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
### Terraform state
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/terraform_state
# gitlab_rails['terraform_state_enabled'] = true
# gitlab_rails['terraform_state_storage_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/terraform_state"
# gitlab_rails['terraform_state_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['terraform_state_object_store_remote_directory'] = "terraform"
# gitlab_rails['terraform_state_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
### CI Secure Files
# gitlab_rails['ci_secure_files_enabled'] = true
# gitlab_rails['ci_secure_files_storage_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/ci_secure_files"
# gitlab_rails['ci_secure_files_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['ci_secure_files_object_store_remote_directory'] = "ci-secure-files"
# gitlab_rails['ci_secure_files_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
### GitLab Pages
# gitlab_rails['pages_object_store_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['pages_object_store_remote_directory'] = "pages"
# gitlab_rails['pages_object_store_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY',
# # # The below options configure an S3 compatible host instead of AWS
# # 'host' => 's3.amazonaws.com',
# # 'aws_signature_version' => 4, # For creation of signed URLs. Set to 2 if provider does not support v4.
# # 'endpoint' => 'https://s3.amazonaws.com', # default: nil - Useful for S3 compliant services such as DigitalOcean Spaces
# # 'path_style' => false # Use 'host/bucket_name/object' instead of 'bucket_name.host/object'
# }
# gitlab_rails['pages_local_store_enabled'] = true
# gitlab_rails['pages_local_store_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/pages"
### Impersonation settings
# gitlab_rails['impersonation_enabled'] = true
### Disable jQuery and CSS animations
# gitlab_rails['disable_animations'] = false
### Application settings cache expiry in seconds. (default: 60)
# gitlab_rails['application_settings_cache_seconds'] = 60
### Usage Statistics
# gitlab_rails['usage_ping_enabled'] = true
### GitLab Mattermost
###! These settings are void if Mattermost is installed on the same omnibus
###! install
# gitlab_rails['mattermost_host'] = "https://mattermost.example.com"
### LDAP Settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/auth/ldap/index.html
###! **Be careful not to break the indentation in the ldap_servers block. It is
###! in yaml format and the spaces must be retained. Using tabs will not work.**
# gitlab_rails['ldap_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['prevent_ldap_sign_in'] = false
###! **remember to close this block with 'EOS' below**
# gitlab_rails['ldap_servers'] = YAML.load <<-'EOS'
# main: # 'main' is the GitLab 'provider ID' of this LDAP server
# label: 'LDAP'
# host: '_your_ldap_server'
# port: 389
# uid: 'sAMAccountName'
# bind_dn: '_the_full_dn_of_the_user_you_will_bind_with'
# password: '_the_password_of_the_bind_user'
# encryption: 'plain' # "start_tls" or "simple_tls" or "plain"
# verify_certificates: true
# smartcard_auth: false
# active_directory: true
# smartcard_ad_cert_field: 'altSecurityIdentities'
# smartcard_ad_cert_format: null # 'issuer_and_serial_number', 'issuer_and_subject' , 'principal_name'
# allow_username_or_email_login: false
# lowercase_usernames: false
# block_auto_created_users: false
# base: ''
# user_filter: ''
# ## EE only
# group_base: ''
# admin_group: ''
# sync_ssh_keys: false
#
# secondary: # 'secondary' is the GitLab 'provider ID' of second LDAP server
# label: 'LDAP'
# host: '_your_ldap_server'
# port: 389
# uid: 'sAMAccountName'
# bind_dn: '_the_full_dn_of_the_user_you_will_bind_with'
# password: '_the_password_of_the_bind_user'
# encryption: 'plain' # "start_tls" or "simple_tls" or "plain"
# verify_certificates: true
# smartcard_auth: false
# active_directory: true
# smartcard_ad_cert_field: 'altSecurityIdentities'
# smartcard_ad_cert_format: null # 'issuer_and_serial_number', 'issuer_and_subject' , 'principal_name'
# allow_username_or_email_login: false
# lowercase_usernames: false
# block_auto_created_users: false
# base: ''
# user_filter: ''
# ## EE only
# group_base: ''
# admin_group: ''
# sync_ssh_keys: false
# EOS
### Smartcard authentication settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/auth/smartcard.html
# gitlab_rails['smartcard_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['smartcard_ca_file'] = "/etc/gitlab/ssl/CA.pem"
# gitlab_rails['smartcard_client_certificate_required_host'] = 'smartcard.gitlab.example.com'
# gitlab_rails['smartcard_client_certificate_required_port'] = 3444
# gitlab_rails['smartcard_required_for_git_access'] = false
# gitlab_rails['smartcard_san_extensions'] = false
### OmniAuth Settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/integration/omniauth.html
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_enabled'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_allow_single_sign_on'] = ['saml']
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_sync_email_from_provider'] = 'saml'
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_sync_profile_from_provider'] = ['saml']
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_sync_profile_attributes'] = ['email']
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_auto_sign_in_with_provider'] = 'saml'
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_block_auto_created_users'] = true
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_auto_link_ldap_user'] = false
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_auto_link_saml_user'] = false
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_auto_link_user'] = ['twitter']
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_external_providers'] = ['twitter', 'google_oauth2']
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_allow_bypass_two_factor'] = ['google_oauth2']
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_providers'] = [
# {
# "name" => "google_oauth2",
# "app_id" => "YOUR APP ID",
# "app_secret" => "YOUR APP SECRET",
# "args" => { "access_type" => "offline", "approval_prompt" => "" }
# }
# ]
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_cas3_session_duration'] = 28800
# gitlab_rails['omniauth_saml_message_max_byte_size'] = 250000
### FortiAuthenticator authentication settings
# gitlab_rails['forti_authenticator_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['forti_authenticator_host'] = 'forti_authenticator.example.com'
# gitlab_rails['forti_authenticator_port'] = 443
# gitlab_rails['forti_authenticator_username'] = 'admin'
# gitlab_rails['forti_authenticator_access_token'] = 's3cr3t'
### FortiToken Cloud authentication settings
# gitlab_rails['forti_token_cloud_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['forti_token_cloud_client_id'] = 'forti_token_cloud_client_id'
# gitlab_rails['forti_token_cloud_client_secret'] = 's3cr3t'
### DuoAuth authentication settings
# gitlab_rails['duo_auth_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['duo_auth_integration_key'] = 'duo_auth_integration_key'
# gitlab_rails['duo_auth_secret_key'] = 'duo_auth_secret_key'
# gitlab_rails['duo_auth_hostname'] = 'duo_auth.example.com'
### Backup Settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/backups.html
# gitlab_rails['manage_backup_path'] = true
# gitlab_rails['backup_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/backups"
# gitlab_rails['backup_gitaly_backup_path'] = "/opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/gitaly-backup"
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/backup_restore/backup_gitlab.html#backup-archive-permissions
# gitlab_rails['backup_archive_permissions'] = 0644
# gitlab_rails['backup_pg_schema'] = 'public'
###! The duration in seconds to keep backups before they are allowed to be deleted
# gitlab_rails['backup_keep_time'] = 604800
# gitlab_rails['backup_upload_connection'] = {
# 'provider' => 'AWS',
# 'region' => 'eu-west-1',
# 'aws_access_key_id' => 'AKIAKIAKI',
# 'aws_secret_access_key' => 'secret123',
# # # If IAM profile use is enabled, remove aws_access_key_id and aws_secret_access_key
# 'use_iam_profile' => false
# }
# gitlab_rails['backup_upload_remote_directory'] = 'my.s3.bucket'
# gitlab_rails['backup_multipart_chunk_size'] = 104857600
###! **Turns on AWS Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys for
###! backups**
# gitlab_rails['backup_encryption'] = 'AES256'
###! The encryption key to use with AWS Server-Side Encryption.
###! Setting this value will enable Server-Side Encryption with customer provided keys;
###! otherwise S3-managed keys are used.
# gitlab_rails['backup_encryption_key'] = '<base64-encoded encryption key>'
###! **Turns on AWS Server-Side Encryption with Amazon SSE-KMS (AWS managed but customer-master key)
# gitlab_rails['backup_upload_storage_options'] = {
# 'server_side_encryption' => 'aws:kms',
# 'server_side_encryption_kms_key_id' => 'arn:aws:kms:YOUR-KEY-ID-HERE'
# }
###! **Specifies Amazon S3 storage class to use for backups. Valid values
###! include 'STANDARD', 'STANDARD_IA', and 'REDUCED_REDUNDANCY'**
# gitlab_rails['backup_storage_class'] = 'STANDARD'
###! Skip parts of the backup. Comma separated.
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/backup_restore/backup_gitlab.html#excluding-specific-data-from-the-backup
#gitlab_rails['env'] = {
# "SKIP" => "db,uploads,repositories,builds,artifacts,lfs,registry,pages"
#}
### For setting up different data storing directory
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#store-git-data-in-an-alternative-directory
###! **If you want to use a single non-default directory to store git data use a
###! path that doesn't contain symlinks.**
# git_data_dirs({
# "default" => {
# "path" => "/mnt/nfs-01/git-data"
# }
# })
### Gitaly settings
# gitlab_rails['gitaly_token'] = 'secret token'
### For storing GitLab application uploads, eg. LFS objects, build artifacts
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/development/shared_files.html
# gitlab_rails['shared_path'] = '/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared'
### For storing encrypted configuration files
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/encrypted_configuration.html
# gitlab_rails['encrypted_settings_path'] = '/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/encrypted_settings'
### Wait for file system to be mounted
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#start-linux-package-installation-services-only-after-a-given-file-system-is-mounted
# high_availability['mountpoint'] = ["/var/opt/gitlab/git-data", "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared"]
### GitLab Shell settings for GitLab
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_ssh_port'] = 22
# gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_git_timeout'] = 800
### Extra customization
# gitlab_rails['extra_google_analytics_id'] = '_your_tracking_id'
# gitlab_rails['extra_google_tag_manager_id'] = '_your_tracking_id'
# gitlab_rails['extra_one_trust_id'] = '_your_one_trust_id'
# gitlab_rails['extra_google_tag_manager_nonce_id'] = '_your_google_tag_manager_id'
# gitlab_rails['extra_bizible'] = false
# gitlab_rails['extra_matomo_url'] = '_your_matomo_url'
# gitlab_rails['extra_matomo_site_id'] = '_your_matomo_site_id'
# gitlab_rails['extra_matomo_disable_cookies'] = false
# gitlab_rails['extra_maximum_text_highlight_size_kilobytes'] = 512
##! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/environment-variables.html
# gitlab_rails['env'] = {
# 'BUNDLE_GEMFILE' => "/opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/Gemfile",
# 'PATH' => "/opt/gitlab/bin:/opt/gitlab/embedded/bin:/bin:/usr/bin"
# }
# gitlab_rails['rack_attack_git_basic_auth'] = {
# 'enabled' => false,
# 'ip_whitelist' => ["127.0.0.1"],
# 'maxretry' => 10,
# 'findtime' => 60,
# 'bantime' => 3600
# }
# gitlab_rails['dir'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails"
# gitlab_rails['log_directory'] = "/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-rails"
# gitlab_rails['log_group'] = nil
#### Change the initial default admin password and shared runner registration tokens.
####! **Only applicable on initial setup, changing these settings after database
####! is created and seeded won't yield any change.**
# gitlab_rails['initial_root_password'] = "password"
# gitlab_rails['initial_shared_runners_registration_token'] = "token"
#### Toggle if root password should be printed to STDOUT during initialization
# gitlab_rails['display_initial_root_password'] = false
#### Toggle if initial root password should be written to /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password
# gitlab_rails['store_initial_root_password'] = true
#### Set path to an initial license to be used while bootstrapping GitLab.
####! **Only applicable on initial setup, future license updates need to be done via UI.
####! Updating the file specified in this path won't yield any change after the first reconfigure run.
# gitlab_rails['initial_license_file'] = '/etc/gitlab/company.gitlab-license'
#### Enable or disable automatic database migrations
# gitlab_rails['auto_migrate'] = true
#### This is advanced feature used by large gitlab deployments where loading
#### whole RAILS env takes a lot of time.
# gitlab_rails['rake_cache_clear'] = true
### GitLab database settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/database.html
###! **Only needed if you use an external database.**
# gitlab_rails['db_adapter'] = "postgresql"
# gitlab_rails['db_encoding'] = "unicode"
# gitlab_rails['db_collation'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_database'] = "gitlabhq_production"
# gitlab_rails['db_username'] = "gitlab"
# gitlab_rails['db_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_host'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_port'] = 5432
# gitlab_rails['db_socket'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_sslmode'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_sslcompression'] = 0
# gitlab_rails['db_sslrootcert'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_sslcert'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_sslkey'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_prepared_statements'] = false
# gitlab_rails['db_statements_limit'] = 1000
# gitlab_rails['db_connect_timeout'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_keepalives'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_keepalives_idle'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_keepalives_interval'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_keepalives_count'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_tcp_user_timeout'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_application_name'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['db_database_tasks'] = true
##! Command to generate extra database configuration
# gitlab_rails['db_extra_config_command'] = nil
### Gitlab decomposed database settings
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/database.html
# gitlab_rails['databases']['main']['db_database'] = 'gitlabhq_production'
# gitlab_rails['databases']['main']['database_tasks'] = true
# gitlab_rails['databases']['ci']['enable'] = true
# gitlab_rails['databases']['ci']['db_database'] = 'gitlabhq_production'
# gitlab_rails['databases']['ci']['database_tasks'] = false
### GitLab ClickHouse connection settings
###! EXPERIMENTAL
# gitlab_rails['clickhouse_databases']['main']['database'] = 'dbname'
# gitlab_rails['clickhouse_databases']['main']['url'] = 'https://example.com/path'
# gitlab_rails['clickhouse_databases']['main']['username'] = 'gitlab'
# gitlab_rails['clickhouse_databases']['main']['password'] = 'password'
### GitLab Redis settings
###! Connect to your own Redis instance
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/redis.html
#### Redis TCP connection
# gitlab_rails['redis_host'] = "127.0.0.1"
# gitlab_rails['redis_port'] = 6379
# gitlab_rails['redis_ssl'] = false
# gitlab_rails['redis_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_database'] = 0
# gitlab_rails['redis_enable_client'] = true
# gitlab_rails['redis_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_connect_timeout'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_read_timeout'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_write_timeout'] = nil
#### Redis local UNIX socket (will be disabled if TCP method is used)
# gitlab_rails['redis_socket'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/redis/redis.socket"
#### Session cookie settings
# gitlab_rails['session_store_session_cookie_token_prefix'] = ''
#### Sentinel support
####! To have Sentinel working, you must enable Redis TCP connection support
####! above and define a few Sentinel hosts below (to get a reliable setup
####! at least 3 hosts).
####! **You don't need to list every sentinel host, but the ones not listed will
####! not be used in a fail-over situation to query for the new master.**
# gitlab_rails['redis_sentinels'] = [
# {'host' => '127.0.0.1', 'port' => 26379},
# ]
# gitlab_rails['redis_sentinels_password'] = 'sentinel-requirepass-goes-here'
# gitlab_rails']['redis_sentinel_master'] = nil
# gitlab_rails']['redis_sentinel_master_ip'] = nil
# gitlab_rails']['redis_sentinel_master_port'] = nil
#### Cluster support
####! Cluster support is only available for selected Redis instances. `resque.yml` will not
####! support cluster mode to maintain full-compatibility with the GitLab rails application.
####!
####! To have Redis Cluster working, you must declare `redis_{instance}_cluster_nodes`
####! `redis_{instance}_username` and `redis_{instance}_password` are required if ACL
####! is enabled for the Redis servers.
# gitlab_rails['redis_xxxx_cluster_nodes'] = [
# {'host' => '127.0.0.1', 'port' => 6379},
# ]
#### Separate instances support
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/redis.html#running-with-multiple-redis-instances
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cache_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_queues_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_shared_state_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_trace_chunks_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_actioncable_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_rate_limiting_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_sessions_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_cluster_rate_limiting_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_repository_cache_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_instance'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_sentinels'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_username'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_password'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_cluster_nodes'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_tls_ca_cert_dir'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/'
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_tls_ca_cert_file'] = '/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/cacert.pem'
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_tls_client_cert_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_tls_client_key_file'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_sentinel_master'] = nil
# gitlab_rails['redis_yml_override'] = nil
################################################################################
## Container Registry settings
##! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/packages/container_registry.html
################################################################################
# registry_external_url 'https://registry.example.com'
### Settings used by GitLab application
# gitlab_rails['registry_enabled'] = true
# gitlab_rails['registry_host'] = "registry.gitlab.example.com"
# gitlab_rails['registry_port'] = "5005"
# gitlab_rails['registry_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/shared/registry"
# Notification secret, it's used to authenticate notification requests to GitLab application
# You only need to change this when you use external Registry service, otherwise
# it will be taken directly from notification settings of your Registry
# gitlab_rails['registry_notification_secret'] = nil
###! **Do not change the following 3 settings unless you know what you are
###! doing**
# gitlab_rails['registry_api_url'] = "http://127.0.0.1:5000"
# gitlab_rails['registry_key_path'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/certificate.key"
# gitlab_rails['registry_issuer'] = "omnibus-gitlab-issuer"
### Settings used by Registry application
# registry['enable'] = true
# registry['username'] = "registry"
# registry['group'] = "registry"
# registry['uid'] = nil
# registry['gid'] = nil
# registry['dir'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/registry"
# registry['registry_http_addr'] = "127.0.0.1:5000"
# registry['debug_addr'] = "localhost:5001"
# registry['log_directory'] = "/var/log/gitlab/registry"
# registry['env_directory'] = "/opt/gitlab/etc/registry/env"
# registry['env'] = {
# 'SSL_CERT_DIR' => "/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/"
# }
# registry['log_level'] = "info"
# registry['log_formatter'] = "text"
# registry['rootcertbundle'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/registry/certificate.crt"
# registry['health_storagedriver_enabled'] = true
# registry['middleware'] = nil
# registry['storage_delete_enabled'] = true
# registry['validation_enabled'] = false
# registry['autoredirect'] = false
# registry['compatibility_schema1_enabled'] = false
# registry['database'] = nil
### Registry backend storage
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/packages/container_registry.html#configure-storage-for-the-container-registry
# registry['storage'] = {
# 's3' => {
# 'accesskey' => 's3-access-key',
# 'secretkey' => 's3-secret-key-for-access-key',
# 'bucket' => 'your-s3-bucket',
# 'region' => 'your-s3-region',
# 'regionendpoint' => 'your-s3-regionendpoint'
# },
# 'redirect' => {
# 'disable' => false
# }
# }
### Registry database
###! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/packages/container_registry_metadata_database.html#new-installations
# registry['database'] = {
# 'enabled' => true,
# 'host' => 'localhost',
# 'port' => 5432,
# 'user' => 'postgres',
# 'password' => 'postgres',
# 'dbname' => 'registry',
# 'sslmode' => 'verify-full',
# 'sslcert' => '/path/to/client.crt',
# 'sslkey' => '/path/to/client.key',
# 'sslrootcert' => '/path/to/root.crt',
# 'connecttimeout' => '5s',
# 'draintimeout' => '2m',
# 'preparedstatements' => false,
# 'primary' => 'primary.record.fqdn',
# 'pool' => {
# 'maxidle' => 25,
# 'maxopen' => 25,
# 'maxlifetime' => '5m'
# }
# }
### Registry garbage collection
###! Docs: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/container-registry/-/blob/master/docs/configuration.md?ref_type=heads#gc
# registry['gc'] = {
# 'disabled' => false,
# 'maxbackoff' => '24h',
# 'noidlebackoff' => false,
# 'transactiontimeout' => '10s',
# 'reviewafter' => '24h',
# 'manifests' => {
# 'disabled' => false,
# 'interval' => '5s'
# },
# 'blobs' => {
# 'disabled' => false,
# 'interval' => '5s',
# 'storagetimeout' => '5s'
# }
# }
### Registry notifications endpoints
# registry['notifications'] = [
# {
# 'name' => 'test_endpoint',
# 'url' => 'https://gitlab.example.com/notify2',
# 'timeout' => '500ms',
# 'threshold' => 5, # DEPRECATED: use maxretries instead https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/container-registry/-/issues/1243
# 'maxretries' => 5,
# 'backoff' => '1s',
# 'headers' => {
# "Authorization" => ["AUTHORIZATION_EXAMPLE_TOKEN"]
# }
# }
# ]
### Default registry notifications
# registry['default_notifications_timeout'] = "500ms"
# registry['default_notifications_threshold'] = 5
# registry['default_notifications_maxretries'] = 5
# registry['default_notifications_backoff'] = "1s"
# registry['default_notifications_headers'] = {}
################################################################################
## Error Reporting and Logging with Sentry
################################################################################
# gitlab_rails['sentry_enabled'] = false
# gitlab_rails['sentry_dsn'] = 'https://<key>@sentry.io/<project>'
# gitlab_rails['sentry_clientside_dsn'] = 'https://<key>@sentry.io/<project>'
# gitlab_rails['sentry_environment'] = 'production'
################################################################################
## CI_JOB_JWT
################################################################################
##! RSA private key used to sign CI_JOB_JWT
# gitlab_rails['ci_jwt_signing_key'] = nil # Will be generated if not set.
################################################################################
## GitLab Workhorse
##! Docs: https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/workhorse/README.md
################################################################################
# gitlab_workhorse['enable'] = true
# gitlab_workhorse['ha'] = false
# gitlab_workhorse['alt_document_root'] = nil
##! Duration to wait for all requests to finish (e.g. "10s" for 10
##! seconds). By default this is disabled to preserve the existing
##! behavior of fast shutdown. This should not be set higher than 30
##! seconds, since gitlab-ctl will wait up to 30 seconds (as defined by
##! the SVWAIT variable) and report a timeout error if the process has
##! not shut down.
# gitlab_workhorse['shutdown_timeout'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['listen_network'] = "unix"
# gitlab_workhorse['listen_umask'] = 000
# gitlab_workhorse['listen_addr'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse/sockets/socket"
# gitlab_workhorse['auth_backend'] = "http://localhost:8080"
##! Enable Redis keywatcher, if this setting is not present it defaults to true
# gitlab_workhorse['workhorse_keywatcher'] = true
##! the empty string is the default in gitlab-workhorse option parser
# gitlab_workhorse['auth_socket'] = "''"
##! put an empty string on the command line
# gitlab_workhorse['pprof_listen_addr'] = "''"
# gitlab_workhorse['prometheus_listen_addr'] = "localhost:9229"
# gitlab_workhorse['dir'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse"
# gitlab_workhorse['log_directory'] = "/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-workhorse"
# gitlab_workhorse['proxy_headers_timeout'] = "1m0s"
##! limit number of concurrent API requests, defaults to 0 which is unlimited
# gitlab_workhorse['api_limit'] = 0
##! limit number of API requests allowed to be queued, defaults to 0 which
##! disables queuing
# gitlab_workhorse['api_queue_limit'] = 0
##! duration after which we timeout requests if they sit too long in the queue
# gitlab_workhorse['api_queue_duration'] = "30s"
##! Long polling duration for job requesting for runners
# gitlab_workhorse['api_ci_long_polling_duration'] = "60s"
##! Propagate X-Request-Id if available. Workhorse will generate a random value otherwise.
# gitlab_workhorse['propagate_correlation_id'] = false
##! A list of CIDR blocks to allow for propagation of correlation ID.
##! propagate_correlation_id should also be set to true.
##! For example: %w(127.0.0.1/32 192.168.0.1/32)
# gitlab_workhorse['trusted_cidrs_for_propagation'] = nil
##! A list of CIDR blocks that must match remote IP addresses to use
##! X-Forwarded-For HTTP header for the actual client IP. Used in
##! conjuction with propagate_correlation_id and
##! trusted_cidrs_for_propagation.
##! For example: %w(127.0.0.1/32 192.168.0.1/32)
# gitlab_workhorse['trusted_cidrs_for_x_forwarded_for'] = nil
##! Log format: default is json, can also be text or none.
# gitlab_workhorse['log_format'] = "json"
# gitlab_workhorse['env_directory'] = "/opt/gitlab/etc/gitlab-workhorse/env"
# gitlab_workhorse['env'] = {
# 'PATH' => "/opt/gitlab/bin:/opt/gitlab/embedded/bin:/bin:/usr/bin",
# 'SSL_CERT_DIR' => "/opt/gitlab/embedded/ssl/certs/"
# }
##! Resource limitations for the dynamic image scaler.
##! Exceeding these thresholds will cause Workhorse to serve images in their original size.
##!
##! Maximum number of scaler processes that are allowed to execute concurrently.
##! It is recommended for this not to exceed the number of CPUs available.
# gitlab_workhorse['image_scaler_max_procs'] = 4
##!
##! Maximum file size in bytes for an image to be considered eligible for rescaling
# gitlab_workhorse['image_scaler_max_filesize'] = 250000
##! Service name used to register GitLab Workhorse as a Consul service
# gitlab_workhorse['consul_service_name'] = 'workhorse'
##! Semantic metadata used when registering GitLab Workhorse as a Consul service
# gitlab_workhorse['consul_service_meta'] = {}
##! Redis settings specific for GitLab Workhorse
##! To be used when Workhorse is supposed to use a different Redis instance than
##! other components. The settings specified here should match
##! `gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_*']` settings, if specified. If not specified,
##! they are inferred from the below values. `gitlab_rails['redis_workhorse_*']`
##! settings tell the Rails app which Redis has channels to publish messages to,
##! and `gitlab_workhorse['redis_*']` tells Workhorse which Redis has channels to
##! subscribe to. Hence, the requirement of the settings to match.
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_socket'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/redis/redis.socket"
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_host'] = "127.0.0.1"
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_port'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_database'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_username'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_password'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_ssl'] = false
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_cluster_nodes'] = []
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_sentinels'] = []
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_sentinels_password'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_sentinel_master'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_sentinel_master_ip'] = nil
# gitlab_workhorse['redis_sentinel_master_port'] = nil
##! Command to generate extra configuration
# gitlab_workhorse['extra_config_command'] = nil
##! Metadata configuration section
# gitlab_workhorse['metadata_zip_reader_limit_bytes'] = nil
################################################################################
## GitLab User Settings
##! Modify default git user.
##! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/omnibus/settings/configuration.html#change-the-name-of-the-git-user-or-group
################################################################################
# user['username'] = "git"
# user['group'] = "git"
# user['uid'] = nil
# user['gid'] = nil
##! The shell for the git user
# user['shell'] = "/bin/sh"
##! The home directory for the git user
# user['home'] = "/var/opt/gitlab"
# user['git_user_name'] = "GitLab"
# user['git_user_email'] = "gitlab@#{node['fqdn']}"
################################################################################
## GitLab Puma
##! Tweak puma settings.
##! Docs: https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/operations/puma.html
################################################################################
# puma['enable'] = true
# puma['ha'] = false
# puma['worker_timeout'] = 60
# puma['worker_processes'] = 2
# puma['min_threads'] = 4
# puma['max_threads'] = 4
### Advanced settings
# puma['listen'] = '127.0.0.1'
# puma['port'] = 8080
# puma['socket'] = '/var/opt/gitlab/gitlab-rails/sockets/gitlab.socket'
# puma['somaxconn'] = 2048
### SSL settings
# puma['ssl_listen'] = nil
# puma['ssl_port'] = nil
# puma['ssl_certificate'] = nil
# puma['ssl_certificate_key'] = nil
# puma['ssl_client_certificate'] = nil
# puma['ssl_cipher_filter'] = nil
# puma['ssl_key_password_command'] = nil
# puma['ssl_verify_mode'] = 'none'
# puma['pidfile'] = '/opt/gitlab/var/puma/puma.pid'
# puma['state_path'] = '/opt/gitlab/var/puma/puma.state'
###! **We do not recommend changing this setting**
# puma['log_directory'] = "/var/log/gitlab/puma"
### **Only change these settings if you understand well what they mean**
###! Docs: https://github.com/schneems/puma_worker_killer
# puma['per_worker_max_memory_mb'] = 1024
# puma['exporter_enabled'] = false
# puma['exporter_address'] = "127.0.0.1"
# puma['exporter_port'] = 8083
# puma['exporter_tls_enabled'] = false
# puma['exporter_tls_cert_path'] = ""
# puma['exporter_tls_key_path'] = ""
# puma['prometheus_scrape_scheme'] = 'http'
# puma['prometheus_scrape_tls_server_name'] = 'localhost'
# puma['prometheus_scrape_tls_skip_verification'] = false
##! Service name used to register Puma as a Consul service
# puma['consul_service_name'] = 'rails'
##! Semantic metadata used when registering Puma as a Consul service
# puma['consul_service_meta'] = {}
################################################################################
## GitLab Sidekiq
################################################################################
##! GitLab allows one to start multiple sidekiq processes. These
##! processes can be used to consume a dedicated set of queues. This
##! can be used to ensure certain queues are able to handle additional workload.
##! https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/administration/sidekiq/extra_sidekiq_processes.html
# sidekiq['enable'] = true
# sidekiq['log_directory'] = "/var/log/gitlab/sidekiq"
# sidekiq['log_format'] = "json"
# sidekiq['shutdown_timeout'] = 4
# sidekiq['interval'] = nil
# sidekiq['concurrency'] = 20
##! GitLab allows route a job to a particular queue determined by an array of ##! routing rules.
##! Each routing rule is a tuple of queue selector query and corresponding queue. By default,
##! the routing rules are not configured (empty array)
# sidekiq['routing_rules'] = []
##! Each entry in the queue_groups array denotes a group of queues that have to be processed by a
##! Sidekiq process. Multiple queues can be processed by the same process by
##! separating them with a comma within the group entry, a `*` will process all queues
# sidekiq['queue_groups'] = ['*']
##! Specifies where Prometheus metrics endpoints should be made available for Sidekiq processes.
# sidekiq['metrics_enabled'] = true
# sidekiq['exporter_log_enabled'] = false
# sidekiq['exporter_tls_enabled'] = false
# sidekiq['exporter_tls_cert_path'] = ""
# sidekiq['exporter_tls_key_path'] = ""
# sidekiq['listen_address'] = "localhost"
# sidekiq['listen_port'] = 8082
##! Specifies where health-check endpoints should be made available for Sidekiq processes.
##! Defaults to the same settings as for Prometheus metrics (see above).
# sidekiq['health_checks_enabled'] = true
# sidekiq['health_checks_listen_address'] = "localhost"
# sidekiq['health_checks_listen_port'] = 8092
##! Service name used to register Sidekiq as a Consul service
# sidekiq['consul_service_name'] = 'sidekiq'
##! Semantic metadata used when registering Sidekiq as a Consul service
# sidekiq['consul_service_meta'] = {}
################################################################################
## gitlab-shell
################################################################################
# gitlab_shell['audit_usernames'] = false
# gitlab_shell['log_level'] = 'INFO'
# gitlab_shell['log_format'] = 'json'
# gitlab_shell['http_settings'] = { user: 'username', password: 'password', ca_file: '/etc/ssl/cert.pem', ca_path: '/etc/pki/tls/certs'}
# gitlab_shell['log_directory'] = "/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-shell"
# gitlab_shell['auth_file'] = "/var/opt/gitlab/.ssh/authorized_keys"
### Migration to Go feature flags
# gitlab_shell['migration'] = { enabled: true, features: [] } # DEPRECATED: see https://gitlab.com/groups/gitlab-org/-/epics/14845.
### Git trace log file.
###! If set, git commands receive GIT_TRACE* environment variables
###! Docs: https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Internals-Environment-Variables#_debugging
###! An absolute path starting with / - the trace output will be appended to
###! that file. It needs to exist so we can check permissions and avoid
###! throwing warnings to the users.
# gitlab_shell['git_trace_log_
gitlab이 구동되면, settings > CI/CD > Runners Expand 버튼 > Project runners > New project runner > Registration token copy 한다. gitlab runner의 values.yaml에 <TOKEN>으로 들어갈 정보이다.

이제 gitlab runner를 helm으로 구성한다.
helm repo add gitlab https://charts.gitlab.io
helm repo update gitlab
helm pull gitlab/gitlab-runner
vi values.yaml # 아래 values.yaml 참조하여 수정
helm upgrade --install gitlab-runner -f values.yaml .image:
registry: nexus-docker.<DOMAIN> # Nexus 주소
image: repository/docker-hosted/gitlab-runner # 이미지 repository
tag: alpine3.19-bleeding # 이미지 tag
useTini: false
magePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
imagePullSecrets: # nexus docker repo credentials
- name: nexus-docker-secret
livenessProbe: {}
readinessProbe: {}
replicas: 1
# git주소
gitlabUrl: https://gitlab.<DOMAIN>/
# gitlab에서 복사한 토큰정보
runnerRegistrationToken: "<TOKEN>"
unregisterRunners: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 3600
concurrent: 10
shutdown_timeout: 0
checkInterval: 30
sessionServer:
enabled: false
rbac:
create: false
generatedServiceAccountName: ""
rules: []
clusterWideAccess: false
serviceAccountAnnotations: {}
podSecurityPolicy:
enabled: false
resourceNames:
- gitlab-runner
imagePullSecrets: []
serviceAccount:
create: false
name: default
annotations: {}
imagePullSecrets: []
metrics:
enabled: false
service:
enabled: false
runners:
config: |
[[runners]]
[runners.kubernetes]
namespace = "cloud-native-app" # app이 배포될 대상 네임스페이스
image = "alpine"
helper_image = "nexus-docker.<DOMAIN>/repository/docker-hosted/gitlab-runner-helper:alpine-latest-x86_64-bleeding" # gitlab-runner-helper 이미지
image_pull_secrets = ["nexus-docker-secret"] # nexus docker registry credentials
configPath: ""
tags: "dev-runner" # 대상 클러스터 구분자
cache: {}
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsNonRoot: true
privileged: false
capabilities:
drop: ["ALL"]
strategy: {}
podSecurityContext:
runAsUser: 100
fsGroup: 65533
resources: {}
affinity: {}
topologySpreadConstraints: {}
runtimeClassName: ""
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
extraEnv: {}
extraEnvFrom: {}
hostAliases: []
deploymentAnnotations: {}
deploymentLabels: {}
deploymentLifecycle: {}
podAnnotations: {}
podLabels: {}
priorityClassName: ""
secrets: []
configMaps: {}
volumeMounts: []
volumes: []
extraObjects: []
정상적으로 runner가 올라오면 gitlab에서 Assigned project runners로 확인이 가능하다.

default serviceaccount를 사용하는데, 권한이 부족하다면 필요한 role과 binding 시킨다.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: pipeline-edit
namespace: cloud-native-app
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: cloud-native-app
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: edit
pipeline 은 .gitlab-ci.yml에 작성한다.
git clone 후 jib:build 하여 nexus에 이미지를 올리고 오픈시프트에 배포(정확히는 이미지교체)하는 파이프라인을 생성해보자.
gitlab에서 project선택 > Build > Pipeline editor > configure pipeline > 아래 스크립트 작성 > commit changes
stages: # List of stages for jobs, and their order of execution
- clone
- build
- deploy
variables:
MAVEN_OPTS: "-Dmaven.repo.local=.m2/repository"
clone-job:
stage: clone
image: alpine/git
script:
- echo "Cloning ..."
- 'git clone $GIT_CLONE_URL/sample/boot-test-app1.git'
- cd boot-test-app1
- git rev-parse --short HEAD
- git rev-parse --short HEAD > commit_sha
- cd ..
artifacts:
untracked: false
when: on_success
access: all
expire_in: 3 days
paths:
- boot-test-app1/*
only:
- dev # dev branch만
- pushes # push event 만
tags:
- dev-runner # 멀티 러너일 경우 대상 러너 지정
compile-job: # This job runs in the compile stage.
stage: build # It only starts when the job in the build stage completes successfully.
image: maven:3.9.9-ibm-semeru-17-focal
script:
- echo "Compiling ..."
- cd boot-test-app1
- export CLONED_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA=$(cat commit_sha)
- echo $CLONED_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA
- mvn clean compile jib:build -Djib.to.tags=$CLONED_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA
tags:
- dev-runner
artifacts:
untracked: false
when: on_success
access: all
expire_in: 3 days
paths:
- boot-test-app1/commit_sha
static-test-job: # This job also runs in the test stage.
stage: build # It can run at the same time as compile-job (in parallel).
script:
- echo "static test code... This will take about 10 seconds."
- sleep 10
- echo "No lint issues found."
tags:
- dev-runner
deploy-job: # This job runs in the deploy stage.
stage: deploy # It only runs when *both* jobs in the compile stage complete successfully.
image: nexus-docker.<도메인>/repository/docker-hosted/openshift-origin-cli:v3.11.0
#environment: production
script:
- echo "Deploying application..."
- export CLONED_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA=$(cat boot-test-app1/commit_sha)
- oc set image deployment/app app=nexus-docker.<도메인>/repository/docker-hosted/gitlab-runner-test:$CLONED_COMMIT_SHORT_SHA -n cloud-native-app
tags:
- dev-runner
$GIT_CLONE_URL과 같은 변수는 gitlab > settings > CI/CD > Variables 에서 설정가능하다. (protected는 체크해제)
파이프라인 실행되면, 각 job별로 진행상태와 결과를 도식으로 확인할 수 있다.
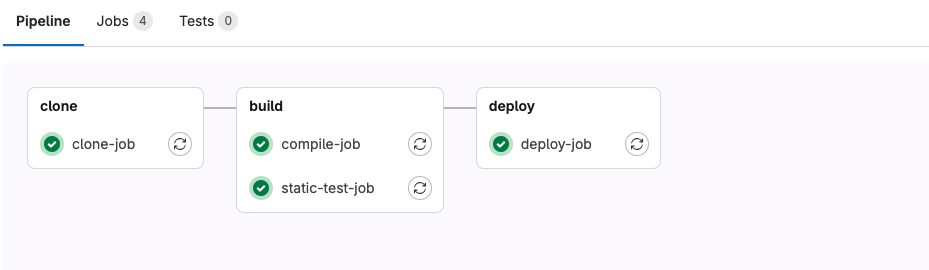
gitlab-runner와 tekton과 비교하자면,
job -> task, artifact -> workspace 와 대응된다고 보면 거의 유사하다.
차이점은 gitlab-runner는 job pod를 termination 시켜주고 로그는 gitlab에서 확인할 수 있다는 부분이 우선 눈에 띄었다.
'CloudNative > App Definition & Developement' 카테고리의 다른 글
| gitlab webhook 생성시 invalid url 에러메시지 (0) | 2025.03.14 |
|---|---|
| argocd applicationSet (2) | 2024.11.26 |
| argocd (0) | 2024.11.25 |
| tekton gradle build + yaml update (0) | 2024.11.21 |
| confluentinc/cp-kafka KRaft yaml (zookeeper out) (2) | 2024.11.20 |